Negative Pressure Pulmonary Edema Treatment
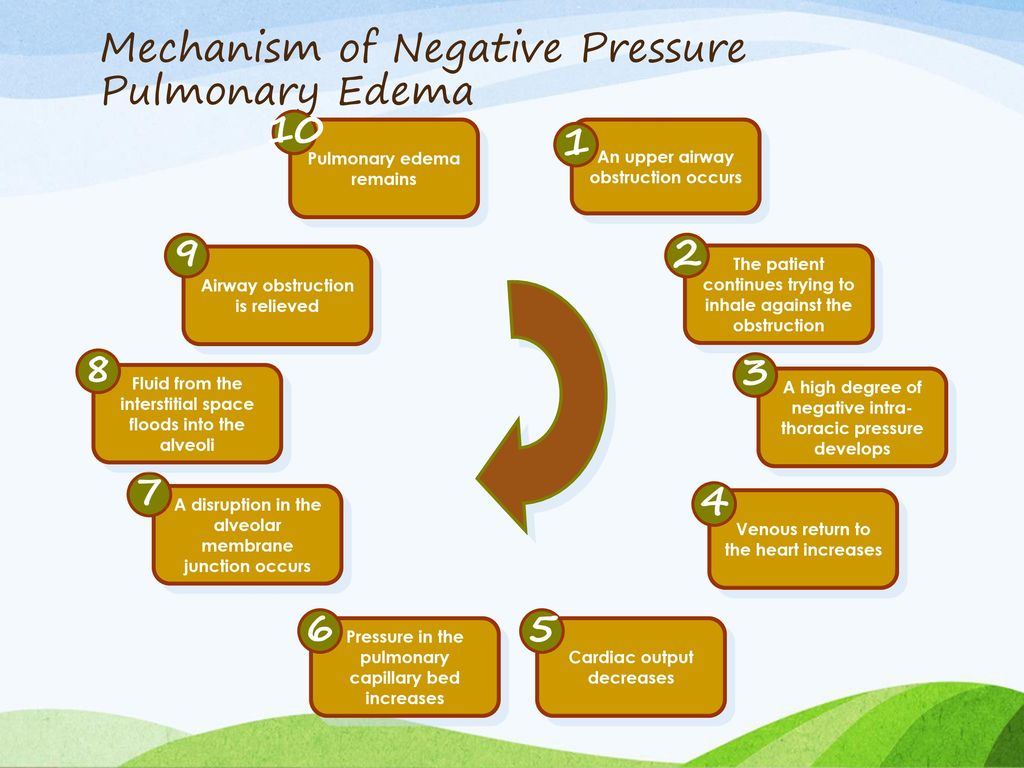
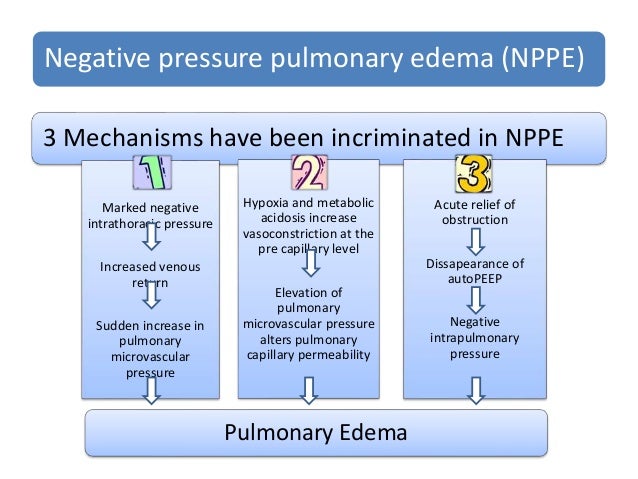
Negative pressure pulmonary edema treatment. NPPE is an example of a noncardiogenic pulmonary edema. The resolution was relatively rapid after reestablishment of the airway adequate oxygenation and positive airway pressure application. Negative-pressure pulmonary edema NPPE is a clinical entity of anaesthesiologic relevance perioperatively caused by obstruction of the conductive airways upper airway obstruction UAO due to laryngospasm in approx.
Patients with NPPE generate very negative airway pressures which augment. Loeb1Xin reviewing the evidence just presented came to the conclusion that the reduction of the negative pressure due to insufflation of air into the lung was the important factor in the prevention or amelioration of pul- monary edema produced by adrenalin. Effective airway management and immediate treatment with oxygen and diuretics is.
Negative pressure pulmonary edema NPPE is an uncommon complication of anesthesia usually resulting from laryngospasm during extubation approximately 01. The events surrounding the development and diagnosis of NPPE will be presented and the treatment modalities will be discussed. The patients history and anesthetic course will be discussed prior to the deveopment of the episode of negative pressure pulmonary edema NPPE.
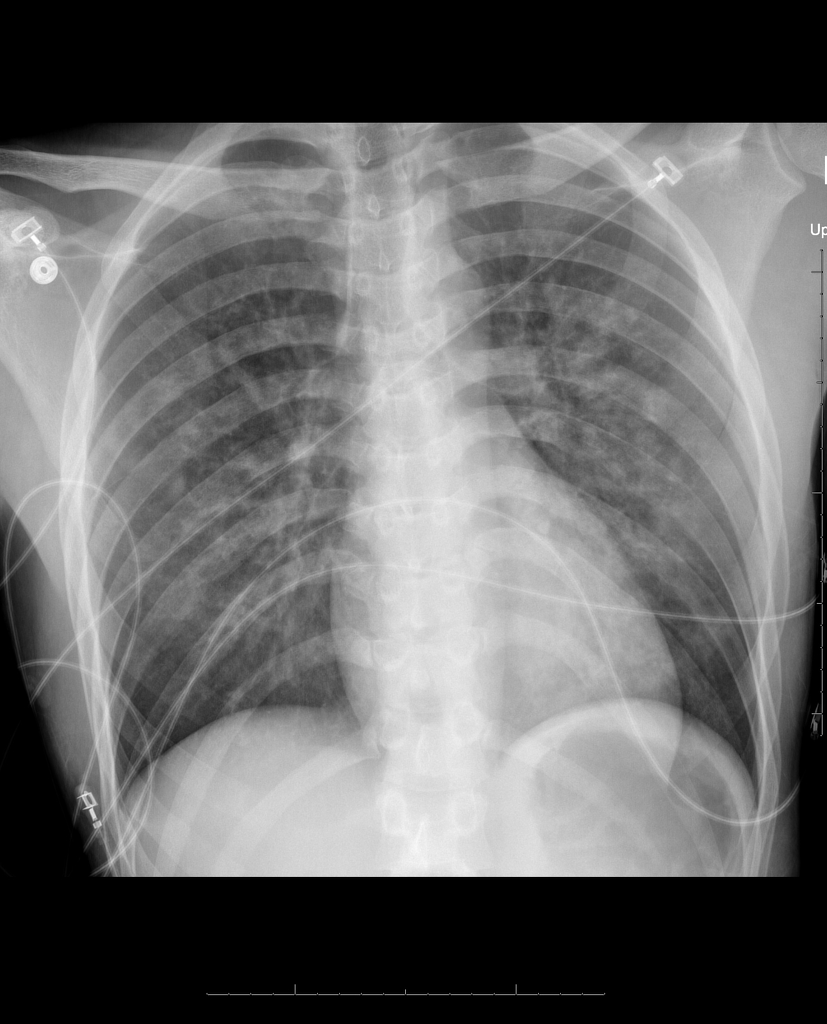
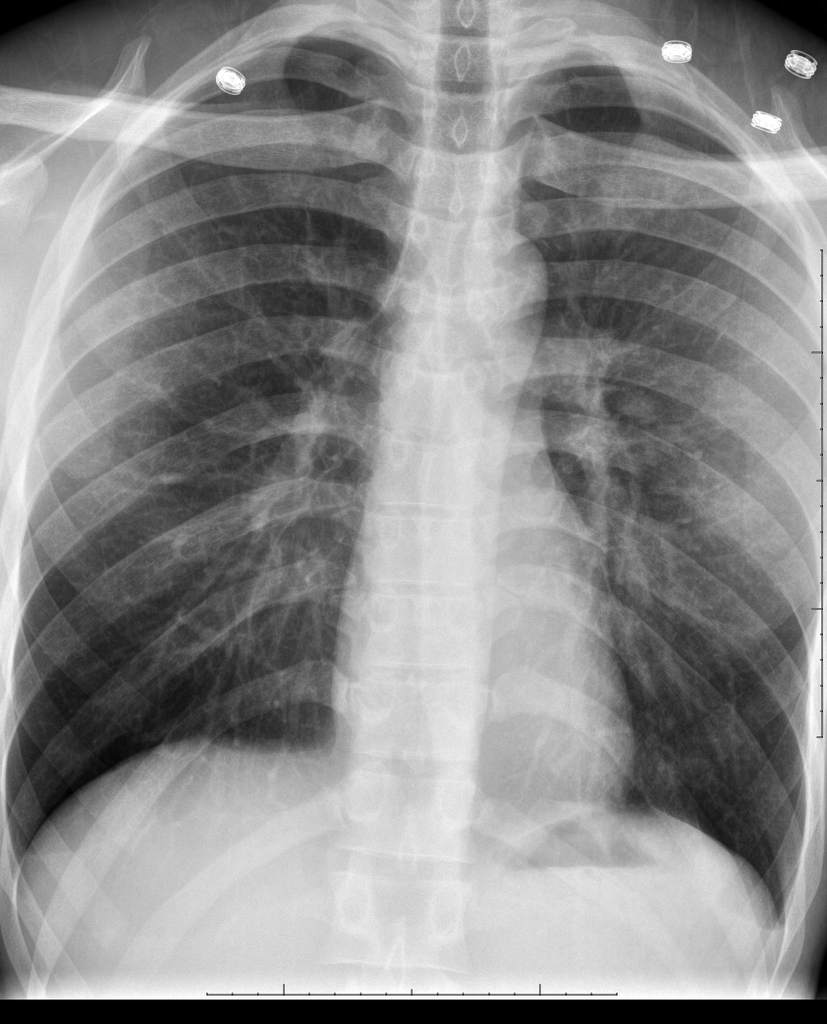
Postoperative day POD 2 her condition became stable computed tomography CT scan indicated the pulmonary edema disappeared. This complication can be severe resulting in death if not diagnosed and treated promptly. Negative pressure pulmonary edema.
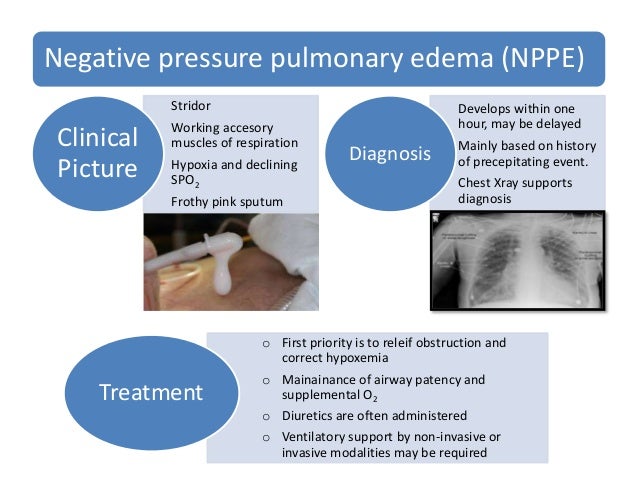
The next step is to address the pulmonary edema with a diuretic unless the patient is hypovolemic. In other words pulmonary edema develops despite the. The first treatment priority is relief of the airway obstruction and correction of hypoxemia.
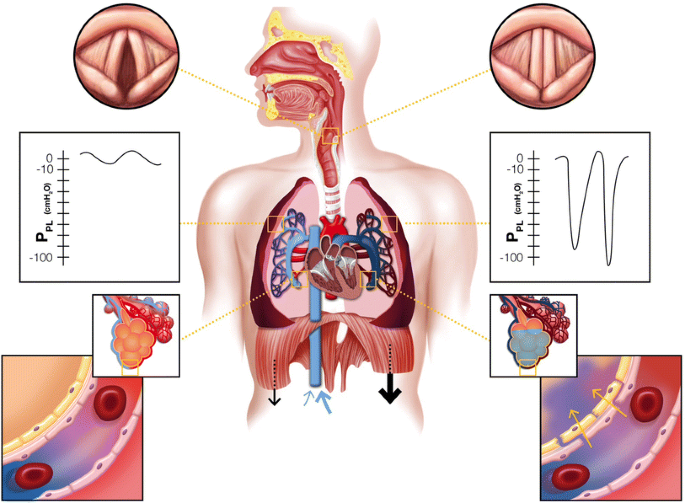
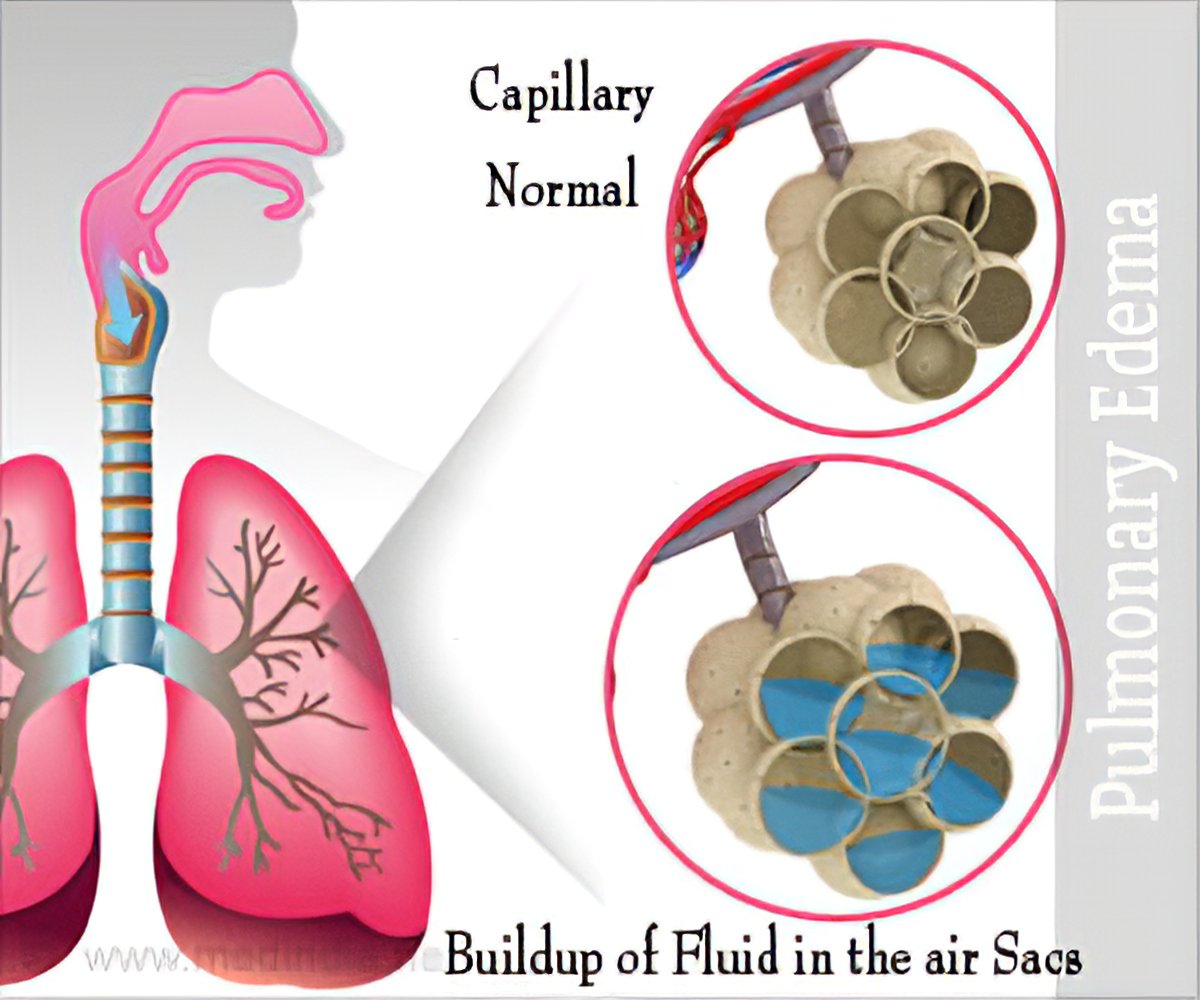
Patients with severe postoperative noncardiogenic pulmonary edema who require mechanical ventilation should be ventilated with a low-tidal volume6administration of positive end-expiratory pressure and low plateau airway pressures78Recent studies suggest that noninvasive respiratory support might be a viable approach for the treatment of patients with postoperative respiratory dysfunction including. Negative-pressure pulmonary edema NPPE or postobstructive pulmonary edema is a well-described cause of acute respiratory failure that occurs after intense inspiratory effort against an obstructed airway usually from upper airway infection tumor or laryngospasm. The patient was undergone assisted ventilation with continuous positive airway pressure CPAP and furosemide 20 mg was given intravenously.
The management of postoperative pulmonary edema usually is aimed at treatment of the underlying cause. Majority of patients give good results with conservative and symptomatic treatment but few do require intubation and initiation of mechanical ventilation with.
Negative pressure pulmonary edema.
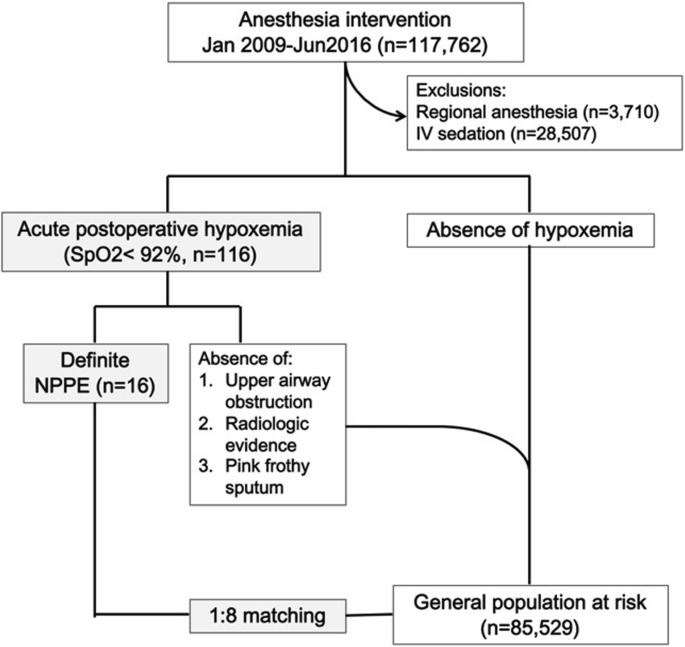
Postobstructive pulmonary edema occurs after relief from an upper airway obstruction and represents a pure form of hydrostatic edema. The management of postoperative pulmonary edema usually is aimed at treatment of the underlying cause. Negative pressure pulmonary edema appeared more frequent in healthy ASA physical status I and II middle-aged and male patients with a general incidence of 0094. Majority of patients give good results with conservative and symptomatic treatment but few do require intubation and initiation of mechanical ventilation with. Loeb1Xin reviewing the evidence just presented came to the conclusion that the reduction of the negative pressure due to insufflation of air into the lung was the important factor in the prevention or amelioration of pul- monary edema produced by adrenalin. NPPE is an example of a noncardiogenic pulmonary edema. It is most frequently caused by an impacted foreign body laryngospasm epiglottitis or strangulation. In other words pulmonary edema develops despite the. 50 of the cases its early recognition and treatment by the anaesthesist is mandatory.
May occur in otherwise healthy individuals who can generate high NIP. Negative-pressure pulmonary edema NPPE is a clinical entity of anaesthesiologic relevance perioperatively caused by obstruction of the conductive airways upper airway obstruction UAO due to laryngospasm in approx. In other words pulmonary edema develops despite the. Typically resolves over 12-48 hours with appropriate care. May occur in otherwise healthy individuals who can generate high NIP. Effective airway management and immediate treatment with oxygen and diuretics is. The patients history and anesthetic course will be discussed prior to the deveopment of the episode of negative pressure pulmonary edema NPPE.




































Posting Komentar untuk "Negative Pressure Pulmonary Edema Treatment"